27.简单地形SimpleTerrainSceneNode类
简单地形的代码完全参考自5.8 基于一个顶点缓冲和一个索引缓冲创建一个地形,代码如下,其中创建地形顶点和索引的方法和获取地形任意点高度的方法没有列出,在后面的解释中给出:
namespace StunEngine.SceneNodes
{
///
/// 基于高度图的简单地形,使用一张漫反射纹理,也可以添加一张细节纹理。
///
public class SimpleTerrainSceneNode : GenericMaterialSceneNode
{
#region 构造函数和成员变量
///
/// 高度图文件名称
///
private string heightMapName;
///
/// 高度图
///
Texture2D heightMap;
///
/// 地形的最小高度
///
private float minimumHeight = float.MaxValue;
///
/// 地形的最大高度
///
private float maximumHeight = float.MinValue;
///
/// 地形高度的缩放值,默认为30,即高度介于0至30之间
///
private float height = 30.0f;
///
/// 地形的宽
///
private int terrainWidth;
///
/// 地形的高
///
private int terrainHeight;
///
/// 高度数据数组
///
float[,] heightData;
///
/// 创建一个默认地形,不使用细节纹理,不缩放
///
/// 引擎
/// 所属场景
/// 高度贴图
/// 颜色贴图
/// 缩放
public SimpleTerrainSceneNode(StunXnaGE engine, Scene setScene, string setHeightMapName, string setColorMap)
: this(engine, setScene, setHeightMapName, setColorMap, null, Vector2 .Zero ,Vector3 .One)
{
}
///
/// 创建一个地形对象。这个对象放置在(0,0,0) - (heightmap width, maxheight, -heightmap height)范围内
///
/// 引擎
/// 所属场景
/// 高度贴图
/// 颜色贴图
/// 地形缩放
/// 包含高度信息的高度图
/// 覆盖在地形上的漫反射纹理。
/// 排列在地形上的细节(噪点)纹理,如果为null则不使用细节贴图。
/// 细节贴图的排列数量
/// 地形缩放
public SimpleTerrainSceneNode(StunXnaGE game, Scene setScene, string setHeightMapName, string setColorMap, string setDetailMap, Vector2 setDetailTiles, Vector3 setScale)
: base(game, setScene,setColorMap ,Vector2 .One ,setDetailMap ,setDetailTiles)
{
this.heightMapName = setHeightMapName;
//将漫反射纹理平铺次数设为8次
this.Material.DiffuseUVTile = new Vector2(8.0f, 8.0f);
//不对地形进行剔除操作
this.DisableCulling = true;
this.DisableUpdateCulling = true;
this.pose.SetScale(ref setScale);
}
#endregion
#region 属性
///
/// 获取高度数据数组
///
public float[,] HeightData { get { return heightData; } }
///
/// 获取范围在[0, infinite]之间的地形最小高度。
///
public float MinHeight
{ get { return minimumHeight; } }
///
/// 获取范围在[0, infinite]之间的地形最大高度。
///
public float MaxHeight{ get { return maximumHeight; } }
///
/// 获取或设置地形高度的缩放值,默认为30,即高度介于0至30之间,这个值改变后需要重新生成地形数据
///
public float Height
{
get { return height; }
set
{
height = value;
//加载高度图数据
heightData = Utility.LoadHeightData(heightMap, ref terrainWidth, ref terrainHeight, ref minimumHeight, ref maximumHeight, height);
CreateTerrain();
}
}
#endregion
#region 重载方法
///
/// 初始化
///
public override void Initialize()
{
this.UpdateOrder = SceneNodeOrdering.Terrain.GetValue();
base.Initialize();
CreateTerrain();
}
internal override void LoadContent()
{
base.LoadContent();
//加载高度图
heightMap = engine.Content.Load(heightMapName);
//加载高度图数据
heightData = Utility.LoadHeightData(heightMap,ref terrainWidth, ref terrainHeight,ref minimumHeight ,ref maximumHeight ,height );
}
///
/// 绘制地形。
///
///
public override int Draw(GameTime gameTime,bool useReflection)
{
// 因为地形上施加了缩放,所以WorldPose.WorldMatrix不正确,需要修正。
this.pose.WorldMatrix = pose.TranslateMatrix;
return base.Draw(gameTime,useReflection);
}
///
/// 如果重置了地形缩放则重新建立地形。
///
public override void OnScaleChange()
{
CreateTerrain();
}
#endregion
#region 单元测试
#if DEBUG
///
/// 测试SimpleTerrainSceneNode类
///
public static void TestSimpleTerrainSceneNode()
{
SimpleTerrainSceneNode terrain = null;
// 相机上一帧的位置。
Vector3 oldPosition=Vector3 .Zero;
TestGame.Start("测试SimpleTerrainSceneNode类",
delegate
{
//添加一个覆盖有草地纹理的地形
terrain = new SimpleTerrainSceneNode(TestGame.engine, TestGame.scene,"Textures\\heightmap128","Textures\\Grass");
TestGame.scene.AddNode(terrain);
//将地形中心放置在坐标原点
Vector3 position=new Vector3(-64,0,64);
terrain.Pose.SetPosition(ref position);
// 开启地形的雾化
terrain .Material.FogEnabled = true;
// 设置雾化颜色
TestGame.scene.FogColor = new Vector4(0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f, 1.0f);
TestGame.engine.BackGroundColor = Color.CornflowerBlue;
//不显示光标
TestGame.scene.IsShowMouse = false;
// 设置点光源和聚光灯
TestGame.scene.sunModel.Visible = false;
position=new Vector3(-15, 20, 0);
TestGame.scene.pointLight.Position = position;
TestGame.scene.pointLightModel.Pose.SetPosition(ref position);
position = new Vector3(0, 20, 0);
TestGame.scene.spotLight .Position = position;
TestGame.scene.spotLightModel .Pose.SetPosition(ref position);
TestGame.scene.floor.Visible = false;
},
delegate
{
// 按数字1键则切换使用的technique
if (Input.KeyboardKeyJustPressed(Keys.D1))
{
if (terrain.Material.CurrentTechniqueName == "SimpleTextured")
terrain.Material.CurrentTechniqueName = "TexturedLights";
else
terrain.Material.CurrentTechniqueName = "SimpleTextured";
}
// 按数字2键则切换地形上的纹理
if (Input.KeyboardKeyJustPressed(Keys.D2))
{
if (terrain.Material.DiffuseTextureName == "Textures\\Grass")
terrain.Material.DiffuseTextureName = "Textures\\Rock";
else
terrain.Material.DiffuseTextureName = "Textures\\Grass";
}
// 按数字3键切换细节纹理的开关
if (Input.KeyboardKeyJustPressed(Keys.D3))
{
if (terrain.Material.DetailTextureName == null)
{
terrain.Material.DetailTextureName = "Textures\\dirty";
terrain.Material.DetailUVTile = new Vector2(8.0f, 8.0f);
}
else
{
terrain.Material.DetailTextureName = null;
terrain.Material.DetailUVTile = Vector2.Zero ;
}
}
// 按数字4键切换地形的高度
if (Input.KeyboardKeyJustPressed(Keys.D4))
{
if (terrain.Height == 30.0f)
terrain.Height = 60.0f;
else
terrain.Height = 30.0f;
}
// 按数字5键切换地形的缩放
if (Input.KeyboardKeyJustPressed(Keys.D5))
{
Vector3 scale=Vector3 .One ;
Vector3 position = new Vector3(-64f, 0f, 64f);
if (terrain.Pose.Scale == scale)
{
scale = new Vector3(2.0f, 2.0f, 2.0f);
terrain.Pose.SetScale(ref scale);
position = new Vector3(-128f, 0f, 128f);
terrain.Pose.SetPosition(ref position);
}
else
{
scale = Vector3.One;
terrain.Pose.SetScale(ref scale );
terrain.Pose.SetPosition(ref position);
}
}
// 实现相机跟随地形的移动
Vector3 camPosition, tempPosition;
TestGame.scene.Camera.GetPosition(out camPosition);
// 如果相机发生移动
if ((camPosition - oldPosition) != Vector3.Zero)
{
// 检查相机与地形的高度差
float height = 5.0f + terrain.GetExactHeightAt(camPosition.X, -camPosition.Z);
float diff = height - camPosition.Y;
if (diff != 0)
{
tempPosition = new Vector3(camPosition.X, height, camPosition.Z);
TestGame.scene.Camera.Pose.SetPosition(ref tempPosition);
TestGame.scene.Camera.UpdateViewMatrix(false);
}
TestGame.scene.Camera.GetPosition(out oldPosition);
}
});
}
#endif
#endregion
}
}
其中Initialize方法中的CreateTerrain()方法代码如下:
////// 基于高度图和缩放创建顶点缓冲和索引缓冲。 /// private void CreateTerrain() { //如果还没有初始化则返回 if (!IsInitialized) return; //顶点声明 VertexDeclaration terrainVertexDeclaration = new VertexDeclaration(engine.GraphicsDevice, VertexPositionNormalTexture.VertexElements); //创建地形顶点 VertexPositionNormalTexture[] terrainVertices = CreateTerrainVertices(); //创建TriangleStrip类型的顶点索引 int[] terrainIndices = CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleStrip(); //创建TriangleList类型的顶点索引 //int[] terrainIndices = CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleList(); // 计算TriangleStrip类型的顶点法线 GenerateNormalsForTriangleStrip(ref terrainVertices, ref terrainIndices); // 计算TriangleList类型的顶点法线 //GenerateNormalsForTriangleList(ref terrainVertices, ref terrainIndices); // 创建顶点缓冲和索引缓冲 VertexBuffer terrainVertexBuffer = new VertexBuffer(engine.GraphicsDevice, VertexPositionNormalTexture.SizeInBytes * terrainVertices.Length, BufferUsage.WriteOnly); terrainVertexBuffer.SetData(terrainVertices); IndexBuffer terrainIndexBuffer = new IndexBuffer(engine.GraphicsDevice, typeof(int), terrainIndices.Length, BufferUsage.WriteOnly); terrainIndexBuffer.SetData(terrainIndices); // 创建TriangleStrip类型的Mesh this.mesh = new Mesh(PrimitiveType.TriangleStrip, terrainVertexBuffer, terrainVertexDeclaration, terrainIndexBuffer, terrainWidth * terrainHeight, terrainWidth * 2 * (terrainHeight - 1) - 2); // 创建TriangleList类型的Mesh //this.mesh = new Mesh(PrimitiveType.TriangleList, terrainVertexBuffer, terrainVertexDeclaration, terrainIndexBuffer, terrainWidth * terrainHeight, (terrainWidth-1) * (terrainHeight-1)*2); pose.GeometryOffset = new Vector3(terrainWidth / 2, 0, terrainWidth / 2); pose.LocalSize = MathHelper.Max(0.1f, terrainWidth); }
具体步骤如下所述。
加载高度图
首先需要加载一张高度图,我使用的高度图如下:

因为后面的高级地形加载高度图的方法相同,所以我将这个方法放在了Utility类的静态方法LoadHeightData中:
////// 加载高度图数据 /// /// 高度图 /// 地形宽度 /// 地形高度 /// 高度图中颜色数据的最小值,通常为0 /// 高度图中颜色数据的最大值,对于8位高度图来说,通常为255 /// 高度的缩放值,表示地形的最大高度 ///返回包含高度图数据的二维数组 public static float[,] LoadHeightData(Texture2D heightMap, ref int terrainWidth, ref int terrainHeight, ref float minimumHeight,ref float maximumHeight,float height) { terrainWidth = heightMap.Width; terrainHeight = heightMap.Height; //先将高度图数据读入到一个一维数组中 Color[] heightMapColors = new Color[terrainWidth * terrainHeight]; heightMap.GetData(heightMapColors); //然后新建一个二维数组 float[,] heightData = new float[terrainWidth, terrainHeight]; //将高度图的红色通道值储存在数组中,因为高度图是一个灰度图,蓝色、绿色通道的值与红色相同,所以储存蓝色、绿色通道的值也可以 for (int x = 0; x < terrainWidth; x++) for (int y = 0; y < terrainHeight; y++) { heightData[x, y] = heightMapColors[x + y * terrainWidth].R; if (heightData[x, y] < minimumHeight) minimumHeight = heightData[x, y]; if (heightData[x, y] > maximumHeight) maximumHeight = heightData[x, y]; } // 重新缩放每个值,这样可以让数组中的值介于0到height的范围中 for (int x = 0; x < terrainWidth; x++) for (int y = 0; y < terrainHeight; y++) heightData[x, y] = (heightData[x, y] - minimumHeight) / (maximumHeight - minimumHeight) * height; return heightData; }
创建地形顶点数据
然后是创建地形顶点CreateTerrainVertices方法:
////// 创建地形顶点 /// ///private VertexPositionNormalTexture[] CreateTerrainVertices() { // 创建一个VertexPositionNormalTexture类型的数组保存所有顶点。地形需要terrainWidth * terrainHeight个顶点。 VertexPositionNormalTexture[] terrainVertices = new VertexPositionNormalTexture[terrainWidth * terrainHeight]; // 在两个循环中创建所有顶点。里面的一个循环创建一行上的顶点,当一行完成后,第一个for循环切换到下一行,直到定义完所有行的顶点。 int i = 0; for (int z = 0; z < terrainHeight; z++) { for (int x = 0; x < terrainWidth; x++) { // 顶点的z值是负的,因此地形是建立在向前(-Z)方向的;顶点的y数据来自于heightData数组;顶点的三个分量都要乘以对应的顶点缩放分量 Vector3 position = new Vector3(x * pose.Scale.X, heightData[x, z] * pose.Scale.Y, -z * pose.Scale.Z); // 先给所有顶点一个默认的法线方向,这个方向马上就会使用GenerateNormals方法替换成正确的方向 Vector3 normal = new Vector3(0, 1, 0); // 指定纹理坐标,即将一张纹理平铺在地形上,纹理的平铺次数是由材质中的DiffuseUVTile决定的,默认设置为8次 Vector2 texCoord = new Vector2((float)x / terrainWidth, (float)z / terrainHeight); terrainVertices[i++] = new VertexPositionNormalTexture(position, normal, texCoord); } } return terrainVertices; }
上面的步骤结果可以用下图表示,为了简单起见,假设高度图的分辨率只有3*3,左图表示顶点序号,右图表示实际高度图的放置:
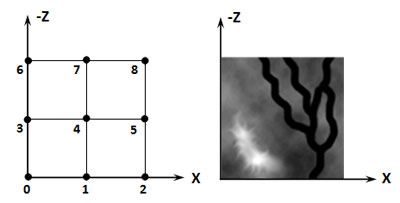
创建地形索引数据
生成TriangleStrip类型的地形顶点索引的方法是CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleStrip。这个代码有点难,对TriangleStrip来说,从第一行开始(自下而上)建立顶点索引的顺序应该是0,3,1,4,2,5(自左向右),但难点是如何切换到第二行?方法是创建退化三角形(Degenerate Triangle,在5.8 基于一个顶点缓冲和一个索引缓冲创建一个地形中叫做Ghost Triangle),退化三角形的面积为零无需绘制,所以不会影响效率,这些退化三角形的顶点不会被发送到显卡,但没有这些退化三角形,建立的TriangleStrip是错误的(在《3D数学基础:图形与游戏开发》一书中P303至P306页也有解释,下载电子书,扫描质量不高)。具体的说,5后面的索引应该这样建立:8,5,7,4,6,3(自右向左),即这两行的索引应是0,3,1,4,2,5,8,5,7,4,6,3,其中2,5,8和5,8,5就是退化三角形,但是使用这种方法有一个缺陷:如果2,5,8三个顶点不在同一高度,对应的三角形面积不为零,仍会被绘制,5.8 基于一个顶点缓冲和一个索引缓冲创建一个地形提及了这个错误,正确的索引顺序应是0,3,1,4,2,5,5,8,4,7,3,6,即退化三角形为2,5,5和5,5,8,但代码中却没有解决这个问题,我也想不出解决的方法,不过好像问题不大。具体代码如下:
////// 创建TriangleStrip类型的地形顶点索引 /// ///private int[] CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleStrip() { //首先创建一个数组,存储地形所需的所有索引。每行需要定义terrainWidth*2个三角形(其中有两个退化三角形),共有terrainHeight - 1行,所以需要terrainWidth * 2 * (terrainHeight - 1)个索引。 int[] terrainIndices = new int[terrainWidth * 2 * (terrainHeight - 1)]; int i = 0; int z = 0; //z值表示当前行。从左向右创建第一行,然后,增加z,表示切换到下一行。第二行从右向左创建,z值仍然增加。这个程序放在while循环中,直到所有偶数行从右向左建立,奇数行从左向右建立。当z变为height-1时while循环结束,返回结果数组。 while (z < terrainHeight - 1) { //奇数行从左向右建立索引 for (int x = 0; x < terrainWidth; x++) { terrainIndices[i++] = x + z * terrainWidth; terrainIndices[i++] = x + (z + 1) * terrainWidth; } z++; //偶数行从右向左建立索引 if (z < terrainHeight - 1) { for (int x = terrainWidth - 1; x >= 0; x--) { terrainIndices[i++] = x + (z + 1) * terrainWidth; terrainIndices[i++] = x + z * terrainWidth; } } z++; } return terrainIndices; }
创建TriangleStrip类型的地形顶点的法线的代码如下,具体解释可参见5.7 自动计算顶点缓冲中所有顶点的法线:
////// 生成TriangleStrip类型的地形顶点的法线 /// /// 顶点数组 /// 索引数组 private void GenerateNormalsForTriangleStrip(ref VertexPositionNormalTexture[] vertices,ref int[] indices) { // 将顶点法线复位到(0,0,0) for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++) vertices[i].Normal = new Vector3(0, 0, 0); //从第三个索引开始,你遇到的每个索引基于索引i, i-1和i-2创建了一个三角形。首先遍历由索引数组定义的所有三角形并创建了两个对应三角形两条边的向量。 //但是,你以TriangleStrip方式定义索引时,每个三角形后会自动反转旋转顺序。结果是,firstVec和secondVec会改变位置,在Cross方法中改变firstVec和secondVec的位置会达到同样效果,每个三角形后都会反转法线的方向。 //你无法改变这个反转,但可以解决这个问题。只需建立一个swappedWinding变量,每个三角形后就反转这个值。如果这个值为true,你就改变法线的方向。 bool swappedWinding = false; for (int i = 2; i < indices.Length; i++) { Vector3 firstVec = vertices[indices[i - 1]].Position - vertices[indices[i]].Position; Vector3 secondVec = vertices[indices[i - 2]].Position - vertices[indices[i]].Position; Vector3 normal = Vector3.Cross(firstVec, secondVec); normal.Normalize(); //如果swappedWinding为true,则改变法线的方向 if (swappedWinding) normal *= -1; //如果firstVec和secondVec向量方向相同,Vector3.Cross方法会发生错误。这种情况下三角形会变成一条线,被称之为ghost三角形(或称之为退化三角形)。这种情况下,Vector3.Cross会返回包含的三个NaN值的Vector3。如果发生这种情况,那么就不要将这个向量添加到顶点,否则会报错。 if (!float.IsNaN(normal.X)) { vertices[indices[i]].Normal += normal; vertices[indices[i - 1]].Normal += normal; vertices[indices[i - 2]].Normal += normal; } //每处理一个三角形后就反转swappedWinding的值 swappedWinding = !swappedWinding; } //归一化法线 for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++) vertices[i].Normal.Normalize(); }
为了比较使用TriangleStrip类型和TriangleList类型的区别,在SimpleTerrainSceneNode类中我也添加了生成TriangleList类型索引的方法CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleList,代码如下,可参见10.2 Terrain类:
////// 创建TriangleList类型的地形顶点索引 /// ///private int[] CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleList() { // 首先创建一个数组,存储地形所需的所有索引。每行需要定义(terrainWidth-1)*2个三角形,共有terrainHeight - 1行,所以需要(terrainWidth - 1) * (terrainHeight - 1) * 6个索引 int[] terrainIndices = new int[(terrainWidth - 1) * (terrainHeight - 1) * 6]; ; int i = 0; for (int z = 0; z < terrainHeight - 1; z++) { for (int x = 0; x < terrainWidth - 1; x++) { // 左下角顶点 int lowerLeft = x + z * terrainWidth; // 右下角顶点 int lowerRight = (x + 1) + z * terrainWidth; // 左上角顶点 int topLeft = x + (z + 1) * terrainWidth; // 右上角顶点 int topRight = (x + 1) + (z + 1) * terrainWidth; //第一个三角形 terrainIndices[i++] = topLeft; terrainIndices[i++] = lowerRight; terrainIndices[i++] = lowerLeft; //第二个三角形 terrainIndices[i++] = topLeft; terrainIndices[i++] = topRight; terrainIndices[i++] = lowerRight; } } return terrainIndices; }
代码中的循环实际上就是生成(以3*3高度图为例)3,1,0;3,4,1;4,2,1;4,5,2;6,4,3;6,7,4;7,5,4;7,8,5的索引,如下图所示:

对应的生成TriangleList类型顶点法线的方法在GenerateNormalsForTriangleList中,可参见5.7 自动计算顶点缓冲中所有顶点的法线:
////// 创建TriangleList类型的地形顶点索引 /// ///private int[] CreateTerrainIndicesForTriangleList() { // 首先创建一个数组,存储地形所需的所有索引。每行需要定义(terrainWidth-1)*2个三角形,共有terrainHeight - 1行,所以需要(terrainWidth - 1) * (terrainHeight - 1) * 6个索引 int[] terrainIndices = new int[(terrainWidth - 1) * (terrainHeight - 1) * 6]; ; int i = 0; for (int z = 0; z < terrainHeight - 1; z++) { for (int x = 0; x < terrainWidth - 1; x++) { // 左下角顶点 int lowerLeft = x + z * terrainWidth; // 右下角顶点 int lowerRight = (x + 1) + z * terrainWidth; // 左上角顶点 int topLeft = x + (z + 1) * terrainWidth; // 右上角顶点 int topRight = (x + 1) + (z + 1) * terrainWidth; //第一个三角形 terrainIndices[i++] = topLeft; terrainIndices[i++] = lowerRight; terrainIndices[i++] = lowerLeft; //第二个三角形 terrainIndices[i++] = topLeft; terrainIndices[i++] = topRight; terrainIndices[i++] = lowerRight; } } return terrainIndices; }
测试下来使用TriangleStrip类型和TriangleList类型绘制速度并没有什么差别,但是使用TriangleStrip类型只需向显卡传递terrainWidth * 2 * (terrainHeight - 1)个索引,如高度图分辨率为128*128,则索引数据量为128*2*127*4=130048个字节,而使用TriangleList类型需要传递terrainWidth - 1) * (terrainHeight - 1) * 6个索引,即127*127*6*4=387096个字节,所以使用TriangleStrip类型可以节省带宽。
注意:你可以注释CreateTerrain()方法中的对应代码行观察使用TriangleStrip类型和TriangleList类型的区别。
使用双线性插值计算地形的精确高度
最后是计算地形精确高度的方法,主要用于相机在地形上的行走,具体的解释请参见5.9 使用双线性插值计算地形的精确高度,代码如下:
////// 判断是否在地形上 /// /// 给定x坐标 /// 给定z坐标 ///private bool IsValidPosition(int x, int z) { return (x >= 0 && x < terrainWidth - 1 && z >= 0 && z < terrainHeight - 1); } /// /// 通过双线性插值获取指定点的精确高度 /// /// /// ///public float GetExactHeightAt(float xCoord, float zCoord) { //--------------------------------------------------------- // // 将给定的xCoord,zCoord坐标转换为地形本地坐标 // //--------------------------------------------------------- // 如果: // P = 世界空间中的坐标 // Tp = 地形在世界空间中的坐标 // Ts = 地形在世界空间中的缩放 // // 那么相对于地形坐标系的位置Tr为 // Tr = ( P - Tp ) / Ts //--------------------------------------------------------- xCoord = (xCoord - pose.Position.X) / pose.Scale.X; zCoord = (zCoord + pose.Position.Z) / pose.Scale.Z; int xLow = (int)xCoord; int zLow = (int)zCoord; // 检查该点是否在地形上。如果不是,返回默认的高度10。 if (!IsValidPosition(xLow, zLow)) { return 10f; } // -------------------------- // 使用双线性插值计算高度 // -------------------------- int xLower = (int)xCoord; int xHigher = xLower + 1; float xRelative = (xCoord - xLower) / ((float)xHigher - (float)xLower); int zLower = (int)zCoord; int zHigher = zLower + 1; float zRelative = (zCoord - zLower) / ((float)zHigher - (float)zLower); float heightLxLz = heightData[xLower, zLower] * pose.Scale.Y+ pose.Position.Y; float heightLxHz = heightData[xLower, zHigher] * pose.Scale.Y + pose.Position.Y; float heightHxLz = heightData[xHigher, zLower] * pose.Scale.Y + pose.Position.Y; float heightHxHz = heightData[xHigher, zHigher] * pose.Scale.Y + pose.Position.Y; // 判断点在左下方三角形中还是在右上方三角形中 bool pointAboveLowerTriangle = (xRelative + zRelative < 1); float finalHeight; // 如果点在左下方的三角形中,这时pointAboveLowerTriangle为true,使用双线性插值获取三角形任意点高度 if (pointAboveLowerTriangle) { finalHeight = heightLxLz; finalHeight += zRelative * (heightLxHz - heightLxLz); finalHeight += xRelative * (heightHxLz - heightLxLz); } //如果该点在右上三角形的内部,这时pointAboveLowerTriangle为false,计算高度的代码有所不同 else { finalHeight = heightHxHz; finalHeight += (1.0f - zRelative) * (heightHxLz - heightHxHz); finalHeight += (1.0f - xRelative) * (heightLxHz - heightHxHz); } return finalHeight; }
单元测试截图如下:
发布时间:2010/4/26 上午11:58:23 阅读次数:8180
