DirectX 10 教程22:绘制到纹理
原文地址:Tutorial 22: Render to Texture(http://www.rastertek.com/dx10tut22.html)。
源代码下载:dx10tut22.zip。
本教程介绍如何实现绘制到纹理,代码基于教程7绘制3D模型和教程11绘制2D图像。
绘制到纹理可以将场景绘制到纹理中而不是通常的后备缓存中,然后你就可以使用这张纹理实现许多效果。例如,你可以从相机的不同角度绘制场景,然后将绘制的纹理作为一个镜像或小屏幕。你也可以对这张纹理进行后期处理或使用shader进行绘制获取独特的效果。利用绘制到纹理所能达到的效果几乎是无限的,因此它也几乎是DirectX 10中威力最大的工具。
但是,因为你将场景绘制了多遍,所以绘制到纹理开销也是巨大的。3D引擎往往在这个阶段开始速度降低,但是相比于它能达到的效果还是物有所值的。
本教程中我们首先将一个旋转的立方体绘制到纹理中,然后将这张纹理绘制到屏幕左上角。立方体也会绘制到屏幕上。纹理的背景设为蓝色。首先看一下更新过的框架。
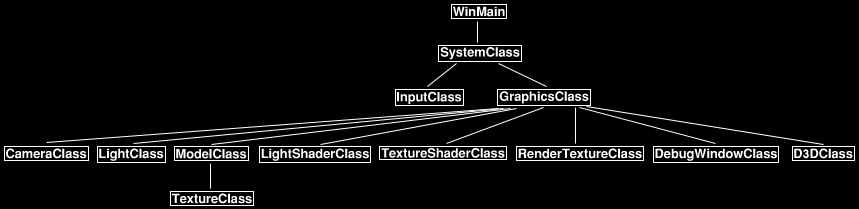
框架
框架中新添了RenderTextureClass和DebugWindowClass。RenderTextureClass封装了DirectX 10中绘制到纹理的功能。DebugWindowClass只是前面教程中BitmapClass类修改个名称而已,但是没有包含纹理,因为我们需要将绘制的纹理作为参数传递到这个类中。我将它命名为DebugWindowClass的原因是我经常使用这个类帮助我调试shader的效果,它可以帮助我看到shader每个阶段的效果。
Rendertextureclass.h
RenderTextureClass将渲染目标设置到纹理而不是常规的后备缓存,还可以从这个类获取以ID3D10ShaderResourceView形式.得到的纹理数据。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: rendertextureclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _RENDERTEXTURECLASS_H_
#define _RENDERTEXTURECLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <d3d10.h>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: RenderTextureClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class RenderTextureClass
{
public:
RenderTextureClass();
RenderTextureClass(const RenderTextureClass&);
~RenderTextureClass();
bool Initialize(ID3D10Device*, int, int);
void Shutdown();
void SetRenderTarget(ID3D10Device*, ID3D10DepthStencilView*);
void ClearRenderTarget(ID3D10Device*, ID3D10DepthStencilView*, float, float, float, float);
ID3D10ShaderResourceView* GetShaderResourceView();
private:
ID3D10Texture2D* m_renderTargetTexture;
ID3D10RenderTargetView* m_renderTargetView;
ID3D10ShaderResourceView* m_shaderResourceView;
};
#endif
Rendertextureclass.cpp
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: rendertextureclass.cpp //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "rendertextureclass.h"
构造函数中将私有指针初始化为null。
RenderTextureClass::RenderTextureClass()
{
m_renderTargetTexture = 0;
m_renderTargetView = 0;
m_shaderResourceView = 0;
}
RenderTextureClass::RenderTextureClass(const RenderTextureClass& other)
{
}
RenderTextureClass::~RenderTextureClass()
{
}
Initialize方法的参数width和height表示要绘制的纹理的大小。注意:如果绘制的是整个屏幕,必须将渲染目标的长宽比设置得和屏幕一样,否则图像会变形。
首先设置纹理描述创建一个渲染目标纹理,然后使用这张纹理创建一个渲染目标视图,这样这张纹理就会以渲染目标的形式进行绘制。最后创建纹理的shader资源视图,这样调用对象就可以访问到这个数据了。
bool RenderTextureClass::Initialize(ID3D10Device* device, int textureWidth, int textureHeight)
{
D3D10_TEXTURE2D_DESC textureDesc;
HRESULT result;
D3D10_RENDER_TARGET_VIEW_DESC renderTargetViewDesc;
D3D10_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC shaderResourceViewDesc;
// Initialize the render target texture description.
ZeroMemory(&textureDesc, sizeof(textureDesc));
// Setup the render target texture description.
textureDesc.Width = textureWidth;
textureDesc.Height = textureHeight;
textureDesc.MipLevels = 1;
textureDesc.ArraySize = 1;
textureDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32A32_FLOAT;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
textureDesc.Usage = D3D10_USAGE_DEFAULT;
textureDesc.BindFlags = D3D10_BIND_RENDER_TARGET | D3D10_BIND_SHADER_RESOURCE;
textureDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
textureDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
// Create the render target texture.
result = device->CreateTexture2D(&textureDesc, NULL, &m_renderTargetTexture);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Setup the description of the render target view.
renderTargetViewDesc.Format = textureDesc.Format;
renderTargetViewDesc.ViewDimension = D3D10_RTV_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
renderTargetViewDesc.Texture2D.MipSlice = 0;
// Create the render target view.
result = device->CreateRenderTargetView(m_renderTargetTexture, &renderTargetViewDesc, &m_renderTargetView);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Setup the description of the shader resource view.
shaderResourceViewDesc.Format = textureDesc.Format;
shaderResourceViewDesc.ViewDimension = D3D10_SRV_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
shaderResourceViewDesc.Texture2D.MostDetailedMip = 0;
shaderResourceViewDesc.Texture2D.MipLevels = 1;
// Create the shader resource view.
result = device->CreateShaderResourceView(m_renderTargetTexture, &shaderResourceViewDesc, &m_shaderResourceView);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
Shutdown释放创建的三个接口。
void RenderTextureClass::Shutdown()
{
if(m_shaderResourceView)
{
m_shaderResourceView->Release();
m_shaderResourceView = 0;
}
if(m_renderTargetView)
{
m_renderTargetView->Release();
m_renderTargetView = 0;
}
if(m_renderTargetTexture)
{
m_renderTargetTexture->Release();
m_renderTargetTexture = 0;
}
return;
}
SetRenderTarget方法将这个类中的渲染目标视图作为当前所有图形绘制的目标。
void RenderTextureClass::SetRenderTarget(ID3D10Device* device, ID3D10DepthStencilView* depthStencilView)
{
// Bind the render target view and depth stencil buffer to the output render pipeline.
device->OMSetRenderTargets(1, &m_renderTargetView, depthStencilView);
return;
}
ClearRenderTarget类似于D3DClass::BeginScene方法,只不过它操作的对象是这个类中的渲染目标视图,这个方法每帧都需要在绘制到渲染目标前进行调用。
void RenderTextureClass::ClearRenderTarget(ID3D10Device* device, ID3D10DepthStencilView* depthStencilView,
float red, float green, float blue, float alpha)
{
float color[4];
// Setup the color to clear the buffer to.
color[0] = red;
color[1] = green;
color[2] = blue;
color[3] = alpha;
// Clear the back buffer.
device->ClearRenderTargetView(m_renderTargetView, color);
// Clear the depth buffer.
device->ClearDepthStencilView(depthStencilView, D3D10_CLEAR_DEPTH, 1.0f, 0);
return;
}
GetShaderResourceView方法以shader资源视图的方式返回绘制到纹理的数据,这样绘制到渲染目标视图的数据就可以作为一张纹理被其他shader使用。你通常会直接将一张纹理传递到shader中,但现在可以调用这个方法达到同样的效果。
ID3D10ShaderResourceView* RenderTextureClass::GetShaderResourceView()
{
return m_shaderResourceView;
}
Debugwindowclass.h
DebugWindowClass几乎就是BitmapClass,但没有了TextureClass类。代码和前面教程中的BitmapClass几乎一样,所以这个类的详细解释可参见前面的教程。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: debugwindowclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _DEBUGWINDOWCLASS_H_
#define _DEBUGWINDOWCLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <d3d10.h>
#include <d3dx10.h>
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: DebugWindowClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class DebugWindowClass
{
private:
struct VertexType
{
D3DXVECTOR3 position;
D3DXVECTOR2 texture;
};
public:
DebugWindowClass();
DebugWindowClass(const DebugWindowClass&);
~DebugWindowClass();
bool Initialize(ID3D10Device*, int, int, int, int);
void Shutdown();
bool Render(ID3D10Device*, int, int);
int GetIndexCount();
private:
bool InitializeBuffers(ID3D10Device*);
void ShutdownBuffers();
bool UpdateBuffers(int, int);
void RenderBuffers(ID3D10Device*);
private:
ID3D10Buffer *m_vertexBuffer, *m_indexBuffer;
int m_vertexCount, m_indexCount;
int m_screenWidth, m_screenHeight;
int m_bitmapWidth, m_bitmapHeight;
int m_previousPosX, m_previousPosY;
};
#endif
Debugwindowclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: debugwindowclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "debugwindowclass.h"
DebugWindowClass::DebugWindowClass()
{
m_vertexBuffer = 0;
m_indexBuffer = 0;
}
DebugWindowClass::DebugWindowClass(const DebugWindowClass& other)
{
}
DebugWindowClass::~DebugWindowClass()
{
}
bool DebugWindowClass::Initialize(ID3D10Device* device, int screenWidth, int screenHeight, int bitmapWidth, int bitmapHeight)
{
bool result;
// Store the screen size.
m_screenWidth = screenWidth;
m_screenHeight = screenHeight;
// Store the size in pixels that this bitmap should be rendered at.
m_bitmapWidth = bitmapWidth;
m_bitmapHeight = bitmapHeight;
// Initialize the previous rendering position to zero.
m_previousPosX = 0;
m_previousPosY = 0;
// Initialize the vertex and index buffer that hold the geometry for the triangle.
result = InitializeBuffers(device);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
void DebugWindowClass::Shutdown()
{
// Release the vertex and index buffers.
ShutdownBuffers();
return;
}
bool DebugWindowClass::Render(ID3D10Device* device, int positionX, int positionY)
{
bool result;
// Re-build the dynamic vertex buffer for rendering to possibly a different location on the screen.
result = UpdateBuffers(positionX, positionY);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Put the vertex and index buffers on the graphics pipeline to prepare them for drawing.
RenderBuffers(device);
return true;
}
int DebugWindowClass::GetIndexCount()
{
return m_indexCount;
}
bool DebugWindowClass::InitializeBuffers(ID3D10Device* device)
{
VertexType* vertices;
unsigned long* indices;
D3D10_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc, indexBufferDesc;
D3D10_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexData, indexData;
HRESULT result;
int i;
// Set the number of vertices in the vertex array.
m_vertexCount = 6;
// Set the number of indices in the index array.
m_indexCount = m_vertexCount;
// Create the vertex array.
vertices = new VertexType[m_vertexCount];
if(!vertices)
{
return false;
}
// Create the index array.
indices = new unsigned long[m_indexCount];
if(!indices)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize vertex array to zeros at first.
memset(vertices, 0, (sizeof(VertexType) * m_vertexCount));
// Load the index array with data.
for(i=0; i<m_indexCount; i++)
{
indices[i] = i;
}
// Set up the description of the dynamic vertex buffer.
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D10_USAGE_DYNAMIC;
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(VertexType) * m_vertexCount;
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D10_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D10_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE;
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
// Give the subresource structure a pointer to the vertex data.
vertexData.pSysMem = vertices;
// Now finally create the vertex buffer.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&vertexBufferDesc, &vertexData, &m_vertexBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Set up the description of the index buffer.
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D10_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(unsigned long) * m_indexCount;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D10_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
// Give the subresource structure a pointer to the index data.
indexData.pSysMem = indices;
// Create the index buffer.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &indexData, &m_indexBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Release the arrays now that the vertex and index buffers have been created and loaded.
delete [] vertices;
vertices = 0;
delete [] indices;
indices = 0;
return true;
}
void DebugWindowClass::ShutdownBuffers()
{
// Release the index buffer.
if(m_indexBuffer)
{
m_indexBuffer->Release();
m_indexBuffer = 0;
}
// Release the vertex buffer.
if(m_vertexBuffer)
{
m_vertexBuffer->Release();
m_vertexBuffer = 0;
}
return;
}
bool DebugWindowClass::UpdateBuffers(int positionX, int positionY)
{
float left, right, top, bottom;
VertexType* vertices;
void* verticesPtr;
HRESULT result;
// If the position we are rendering this bitmap to has not changed then don't update the vertex buffer since it
// currently has the correct parameters.
if((positionX == m_previousPosX) && (positionY == m_previousPosY))
{
return true;
}
// If it has changed then update the position it is being rendered to.
m_previousPosX = positionX;
m_previousPosY = positionY;
// Calculate the screen coordinates of the left side of the bitmap.
left = (float)((m_screenWidth / 2) * -1) + (float)positionX;
// Calculate the screen coordinates of the right side of the bitmap.
right = left + (float)m_bitmapWidth;
// Calculate the screen coordinates of the top of the bitmap.
top = (float)(m_screenHeight / 2) - (float)positionY;
// Calculate the screen coordinates of the bottom of the bitmap.
bottom = top - (float)m_bitmapHeight;
// Create the vertex array.
vertices = new VertexType[m_vertexCount];
if(!vertices)
{
return false;
}
// Load the vertex array with data.
// First triangle.
vertices[0].position = D3DXVECTOR3(left, top, 0.0f); // Top left.
vertices[0].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(0.0f, 0.0f);
vertices[1].position = D3DXVECTOR3(right, bottom, 0.0f); // Bottom right.
vertices[1].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(1.0f, 1.0f);
vertices[2].position = D3DXVECTOR3(left, bottom, 0.0f); // Bottom left.
vertices[2].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(0.0f, 1.0f);
// Second triangle.
vertices[3].position = D3DXVECTOR3(left, top, 0.0f); // Top left.
vertices[3].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(0.0f, 0.0f);
vertices[4].position = D3DXVECTOR3(right, top, 0.0f); // Top right.
vertices[4].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(1.0f, 0.0f);
vertices[5].position = D3DXVECTOR3(right, bottom, 0.0f); // Bottom right.
vertices[5].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(1.0f, 1.0f);
// Initialize the vertex buffer pointer to null first.
verticesPtr = 0;
// Lock the vertex buffer.
result = m_vertexBuffer->Map(D3D10_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, (void**)&verticesPtr);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Copy the data into the vertex buffer.
memcpy(verticesPtr, (void*)vertices, (sizeof(VertexType) * m_vertexCount));
// Unlock the vertex buffer.
m_vertexBuffer->Unmap();
// Release the vertex array as it is no longer needed.
delete [] vertices;
vertices = 0;
return true;
}
void DebugWindowClass::RenderBuffers(ID3D10Device* device)
{
unsigned int stride;
unsigned int offset;
// Set vertex buffer stride and offset.
stride = sizeof(VertexType);
offset = 0;
// Set the vertex buffer to active in the input assembler so it can be rendered.
device->IASetVertexBuffers(0, 1, &m_vertexBuffer, &stride, &offset);
// Set the index buffer to active in the input assembler so it can be rendered.
device->IASetIndexBuffer(m_indexBuffer, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
// Set the type of primitive that should be rendered from this vertex buffer, in this case triangles.
device->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D10_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
return;
}
D3dclass.h
D3Dclass的变化很小。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: d3dclass.h //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifndef _D3DCLASS_H_ #define _D3DCLASS_H_ ///////////// // LINKING // ///////////// #pragma comment(lib, "d3d10.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "d3dx10.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "dxgi.lib") ////////////// // INCLUDES // ////////////// #include#include //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Class name: D3DClass //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// class D3DClass { public: D3DClass(); D3DClass(const D3DClass&); ~D3DClass(); bool Initialize(int, int, bool, HWND, bool, float, float); void Shutdown(); void BeginScene(float, float, float, float); void EndScene(); ID3D10Device* GetDevice();
添加一个新方法用于访问深度模板视图。
ID3D10DepthStencilView* GetDepthStencilView(); void GetProjectionMatrix(D3DXMATRIX&); void GetWorldMatrix(D3DXMATRIX&); void GetOrthoMatrix(D3DXMATRIX&); void TurnZBufferOn(); void TurnZBufferOff();
新添了一个方法用于设置渲染目标。
void SetBackBufferRenderTarget(); private: bool m_vsync_enabled; ID3D10Device* m_device; IDXGISwapChain* m_swapChain; ID3D10RenderTargetView* m_renderTargetView; ID3D10Texture2D* m_depthStencilBuffer; ID3D10DepthStencilState* m_depthStencilState; ID3D10DepthStencilView* m_depthStencilView; ID3D10RasterizerState* m_rasterState; D3DXMATRIX m_projectionMatrix; D3DXMATRIX m_worldMatrix; D3DXMATRIX m_orthoMatrix; ID3D10DepthStencilState* m_depthDisabledStencilState; }; #endif
D3dclass.cpp
下面的代码只包含与上一个教程不同的部分。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: d3dclass.cpp //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "d3dclass.h"
GetDepthStencilView让调用对象可以访问深度模板视图。
ID3D10DepthStencilView* D3DClass::GetDepthStencilView()
{
return m_depthStencilView;
}
SetBackBufferRenderTarget方法会将这个类中的后备缓存作为当前的渲染目标,这个方法通常在绘制到纹理完成后进行,此时我们需要重新将场景绘制到后备缓存中。
void D3DClass::SetBackBufferRenderTarget()
{
// Bind the render target view and depth stencil buffer to the output render pipeline.
m_device->OMSetRenderTargets(1, &m_renderTargetView, m_depthStencilView);
return;
}
Graphicsclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: graphicsclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _GRAPHICSCLASS_H_
#define _GRAPHICSCLASS_H_
/////////////
// GLOBALS //
/////////////
const bool FULL_SCREEN = true;
const bool VSYNC_ENABLED = true;
const float SCREEN_DEPTH = 1000.0f;
const float SCREEN_NEAR = 0.1f;
///////////////////////
// MY CLASS INCLUDES //
///////////////////////
#include "d3dclass.h"
#include "cameraclass.h"
#include "modelclass.h"
#include "lightshaderclass.h"
#include "lightclass.h"
#include "rendertextureclass.h"
#include "debugwindowclass.h"
#include "textureshaderclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: GraphicsClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class GraphicsClass
{
public:
GraphicsClass();
GraphicsClass(const GraphicsClass&);
~GraphicsClass();
bool Initialize(int, int, HWND);
void Shutdown();
bool Frame();
bool Render();
新添了两个私有方法,我们需要将绘制分成两个pass(一次绘制到纹理,一次普通绘制)。
private: void RenderToTexture(); void RenderScene(); private: D3DClass* m_D3D; CameraClass* m_Camera; ModelClass* m_Model; LightShaderClass* m_LightShader; LightClass* m_Light; RenderTextureClass* m_RenderTexture; DebugWindowClass* m_DebugWindow; TextureShaderClass* m_TextureShader; }; #endif
Graphicsclass.cpp
下面的代码只包含与上一个教程不同的部分。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: graphicsclass.cpp //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "graphicsclass.h"
在构造函数中将私有变量初始化为null。
GraphicsClass::GraphicsClass()
{
m_D3D = 0;
m_Camera = 0;
m_Model = 0;
m_LightShader = 0;
m_Light = 0;
m_RenderTexture = 0;
m_DebugWindow = 0;
m_TextureShader = 0;
}
GraphicsClass::GraphicsClass(const GraphicsClass& other)
{
}
GraphicsClass::~GraphicsClass()
{
}
bool GraphicsClass::Initialize(int screenWidth, int screenHeight, HWND hwnd)
{
bool result;
// Create the Direct3D object.
m_D3D = new D3DClass;
if(!m_D3D)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the Direct3D object.
result = m_D3D->Initialize(screenWidth, screenHeight, VSYNC_ENABLED, hwnd, FULL_SCREEN, SCREEN_DEPTH, SCREEN_NEAR);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize Direct3D.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create the camera object.
m_Camera = new CameraClass;
if(!m_Camera)
{
return false;
}
// Create the model object.
m_Model = new ModelClass;
if(!m_Model)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the model object.
result = m_Model->Initialize(m_D3D->GetDevice(), L"../Engine/data/seafloor.dds", "../Engine/data/cube.txt");
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the model object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create the light shader object.
m_LightShader = new LightShaderClass;
if(!m_LightShader)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the light shader object.
result = m_LightShader->Initialize(m_D3D->GetDevice(), hwnd);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the light shader object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create the light object.
m_Light = new LightClass;
if(!m_Light)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the light object.
m_Light->SetDiffuseColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
m_Light->SetDirection(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
创建并初始化render to texture对象。初始化的参数中纹理的大小我使用的是屏幕的大小,表示我想将整个屏幕的画面绘制到相同大小的纹理中。
// Create the render to texture object.
m_RenderTexture = new RenderTextureClass;
if(!m_RenderTexture)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the render to texture object.
result = m_RenderTexture->Initialize(m_D3D->GetDevice(), screenWidth, screenHeight);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
创建并初始化debug window对象。注意我将窗口大小设置为100x100,显然这样做会使图像变形,想要不变形,你只需将上述大小的长宽比设置得和屏幕的长宽比一致即可。
// Create the debug window object.
m_DebugWindow = new DebugWindowClass;
if(!m_DebugWindow)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the debug window object.
result = m_DebugWindow->Initialize(m_D3D->GetDevice(), screenWidth, screenHeight, 100, 100);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the debug window object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create the texture shader object.
m_TextureShader = new TextureShaderClass;
if(!m_TextureShader)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the texture shader object.
result = m_TextureShader->Initialize(m_D3D->GetDevice(), hwnd);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the texture shader object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
return true;
}
void GraphicsClass::Shutdown()
{
// Release the texture shader object.
if(m_TextureShader)
{
m_TextureShader->Shutdown();
delete m_TextureShader;
m_TextureShader = 0;
}
在Shutdown方法中释放DebugWindowClass和RenderTextureClass对象。
// Release the debug window object.
if(m_DebugWindow)
{
m_DebugWindow->Shutdown();
delete m_DebugWindow;
m_DebugWindow = 0;
}
// Release the render to texture object.
if(m_RenderTexture)
{
m_RenderTexture->Shutdown();
delete m_RenderTexture;
m_RenderTexture = 0;
}
// Release the light object.
if(m_Light)
{
delete m_Light;
m_Light = 0;
}
// Release the light shader object.
if(m_LightShader)
{
m_LightShader->Shutdown();
delete m_LightShader;
m_LightShader = 0;
}
// Release the model object.
if(m_Model)
{
m_Model->Shutdown();
delete m_Model;
m_Model = 0;
}
// Release the camera object.
if(m_Camera)
{
delete m_Camera;
m_Camera = 0;
}
// Release the Direct3D object.
if(m_D3D)
{
m_D3D->Shutdown();
delete m_D3D;
m_D3D = 0;
}
return;
}
bool GraphicsClass::Frame()
{
// Set the position of the camera.
m_Camera->SetPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, -5.0f);
return true;
}
bool GraphicsClass::Render()
{
D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, viewMatrix, orthoMatrix;
bool result;
第一个pass绘制到纹理。
// Render the entire scene to the texture first. RenderToTexture();
第二个pass进行普通的绘制。
// Clear the buffers to begin the scene. m_D3D->BeginScene(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); // Render the scene as normal to the back buffer. RenderScene();
绘制完成后将debug window作为2D图像绘制在屏幕50x50的位置。
// Turn off the Z buffer to begin all 2D rendering.
m_D3D->TurnZBufferOff();
// Get the world, view, and ortho matrices from the camera and d3d objects.
m_D3D->GetWorldMatrix(worldMatrix);
m_Camera->GetViewMatrix(viewMatrix);
m_D3D->GetOrthoMatrix(orthoMatrix);
// Put the debug window vertex and index buffers on the graphics pipeline to prepare them for drawing.
result = m_DebugWindow->Render(m_D3D->GetDevice(), 50, 50);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Render the debug window using the texture shader.
m_TextureShader->Render(m_D3D->GetDevice(), m_DebugWindow->GetIndexCount(), worldMatrix, viewMatrix, orthoMatrix,
m_RenderTexture->GetShaderResourceView());
// Turn the Z buffer back on now that all 2D rendering has completed.
m_D3D->TurnZBufferOn();
// Present the rendered scene to the screen.
m_D3D->EndScene();
return true;
}
RenderToTexture方法将渲染目标视图作为当前的渲染目标,绘制完毕后使用D3Dclass对象将渲染目标重新设置为后备缓存。
void GraphicsClass::RenderToTexture()
{
// Set the render target to be the render to texture.
m_RenderTexture->SetRenderTarget(m_D3D->GetDevice(), m_D3D->GetDepthStencilView());
将渲染纹理的背景清除为蓝色,这样我们就可以把它与常规的场景绘制区分开来。
// Clear the render to texture. m_RenderTexture->ClearRenderTarget(m_D3D->GetDevice(), m_D3D->GetDepthStencilView(), 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); // Render the scene now and it will draw to the render to texture instead of the back buffer. RenderScene(); // Reset the render target back to the original back buffer and not the render to texture anymore. m_D3D->SetBackBufferRenderTarget(); return; }
RenderScene方法绘制整个场景。本教程中我们在RenderToTexture中调用它一次,将场景绘制到一张纹理中。然后再Render方法中再调用一次将场景绘制到常规的后备缓存中。
void GraphicsClass::RenderScene()
{
D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix;
static float rotation = 0.0f;
// Generate the view matrix based on the camera's position.
m_Camera->Render();
// Get the world, view, and projection matrices from the camera and d3d objects.
m_D3D->GetWorldMatrix(worldMatrix);
m_Camera->GetViewMatrix(viewMatrix);
m_D3D->GetProjectionMatrix(projectionMatrix);
// Update the rotation variable each frame.
rotation += (float)D3DX_PI * 0.005f;
if(rotation > 360.0f)
{
rotation -= 360.0f;
}
D3DXMatrixRotationY(&worldMatrix, rotation);
// Put the model vertex and index buffers on the graphics pipeline to prepare them for drawing.
m_Model->Render(m_D3D->GetDevice());
// Render the model using the light shader.
m_LightShader->Render(m_D3D->GetDevice(), m_Model->GetIndexCount(), worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix,
m_Model->GetTexture(), m_Light->GetDirection(), m_Light->GetDiffuseColor());
return;
}
总结
现在你理解了绘制到纹理的基本方法。

练习
1.编译并运行程序,你会看到一个旋转的立方体,并且在屏幕左上角显示一个蓝色背景的小立方体,这是绘制到纹理的效果。
2.修改debug window,使它的长宽比与屏幕的长宽比相同。
3.修改3D场景,确认也能正确地绘制到纹理。
4.修改相机的观察角度观察效果。
5.使用这个纹理作为你自己的shader的输入并改变输出结果(例如添加噪点、扫描行等效果)。
文件下载(已下载 1157 次)发布时间:2012/8/10 上午12:28:54 阅读次数:10534
