DirectX 10 教程12:文字引擎
原文地址:Tutorial 12: Font Engine(http://www.rastertek.com/dx10tut12.html)。
源代码:dx10tut12.zip。
在屏幕上绘制文字是任何一个程序非常重要的功能。在DirectX 10中绘制2D文字需要首先理解如何绘制2D图像,这在上一个教程中已经介绍过了,而这教程基于上一个教程。
首先需要一张字体图像,我制作的这张非常简单,它包含所需的字符,是一张1024x16大小的DDS纹理:
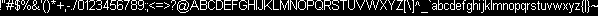
如你所见,这张纹理包含了所需的基本字符。现在你可以构建一个简单的文字引擎了,这个引擎使用一个指向这个纹理的索引绘制单独的字符,原理是绘制一个矩形然后将纹理中的字符绘制到这个矩形上。如果显示的是一个句子,则每个字符对应一个矩形,因此我们需要获取这个句子包含的字符,每个字符使用一个矩形,然后将字符绘制到这些矩形中,最后将所有矩形绘制到屏幕上构成这个句子。
纹理的索引是一个文本文件,包含纹理中字符的位置和大小。这个文本文件让文字引擎可以快速地从纹理中提取字符对应的像素。
下面就是索引文件的内容。文件的格式为:[字符的Ascii码] [字符] [左边的纹理U坐标] [右边的纹理U坐标] [字符的像素宽度]
32 0.0 0.0 0
33 ! 0.0 0.000976563 1
34 " 0.00195313 0.00488281 3
35 # 0.00585938 0.0136719 8
36 $ 0.0146484 0.0195313 5
37 % 0.0205078 0.0302734 10
38 & 0.03125 0.0390625 8
39 ' 0.0400391 0.0410156 1
40 ( 0.0419922 0.0449219 3
41 ) 0.0458984 0.0488281 3
42 * 0.0498047 0.0546875 5
43 + 0.0556641 0.0625 7
44 , 0.0634766 0.0644531 1
45 - 0.0654297 0.0683594 3
46 . 0.0693359 0.0703125 1
47 / 0.0712891 0.0751953 4
48 0 0.0761719 0.0820313 6
49 1 0.0830078 0.0859375 3
50 2 0.0869141 0.0927734 6
51 3 0.09375 0.0996094 6
52 4 0.100586 0.106445 6
53 5 0.107422 0.113281 6
54 6 0.114258 0.120117 6
55 7 0.121094 0.126953 6
56 8 0.12793 0.133789 6
57 9 0.134766 0.140625 6
58 : 0.141602 0.142578 1
59 ; 0.143555 0.144531 1
60 < 0.145508 0.151367 6
61 = 0.152344 0.15918 7
62 > 0.160156 0.166016 6
63 ? 0.166992 0.171875 5
64 @ 0.172852 0.18457 12
65 A 0.185547 0.194336 9
66 B 0.195313 0.202148 7
67 C 0.203125 0.209961 7
68 D 0.210938 0.217773 7
69 E 0.21875 0.225586 7
70 F 0.226563 0.232422 6
71 G 0.233398 0.241211 8
72 H 0.242188 0.249023 7
73 I 0.25 0.250977 1
74 J 0.251953 0.256836 5
75 K 0.257813 0.265625 8
76 L 0.266602 0.272461 6
77 M 0.273438 0.282227 9
78 N 0.283203 0.290039 7
79 O 0.291016 0.298828 8
80 P 0.299805 0.306641 7
81 Q 0.307617 0.31543 8
82 R 0.316406 0.323242 7
83 S 0.324219 0.331055 7
84 T 0.332031 0.338867 7
85 U 0.339844 0.34668 7
86 V 0.347656 0.356445 9
87 W 0.357422 0.370117 13
88 X 0.371094 0.37793 7
89 Y 0.378906 0.385742 7
90 Z 0.386719 0.393555 7
91 [ 0.394531 0.396484 2
92 \ 0.397461 0.401367 4
93 ] 0.402344 0.404297 2
94 ^ 0.405273 0.410156 5
95 _ 0.411133 0.417969 7
96 ` 0.418945 0.420898 2
97 a 0.421875 0.426758 5
98 b 0.427734 0.432617 5
99 c 0.433594 0.438477 5
100 d 0.439453 0.444336 5
101 e 0.445313 0.450195 5
102 f 0.451172 0.455078 4
103 g 0.456055 0.460938 5
104 h 0.461914 0.466797 5
105 i 0.467773 0.46875 1
106 j 0.469727 0.472656 3
107 k 0.473633 0.478516 5
108 l 0.479492 0.480469 1
109 m 0.481445 0.490234 9
110 n 0.491211 0.496094 5
111 o 0.49707 0.501953 5
112 p 0.50293 0.507813 5
113 q 0.508789 0.513672 5
114 r 0.514648 0.517578 3
115 s 0.518555 0.523438 5
116 t 0.524414 0.527344 3
117 u 0.52832 0.533203 5
118 v 0.53418 0.539063 5
119 w 0.540039 0.548828 9
120 x 0.549805 0.554688 5
121 y 0.555664 0.560547 5
122 z 0.561523 0.566406 5
123 { 0.567383 0.570313 3
124 | 0.571289 0.572266 1
125 } 0.573242 0.576172 3
126 ~ 0.577148 0.583984 7
有了索引文件和纹理文件,我们就可以构建文字引擎了。如果你想生成自己的索引文件,只需确保每个字符由空格分隔,你可以自己编写一个位图转换程序创建纹理的TU和TV坐标。
别忘了不同用户运行程序的分辨率可能不同。同一大小的文字不会在所有的分辨率下都能清晰显示,所以你需要制作几种不同大小的字体,根据分辨率灵活地使用其中的一种才能达到最好的效果。
框架
因为我们需要封装文字的功能,所以需要在框架中添加几个新类。更新后的框架如下图所示:
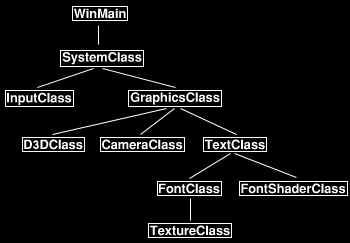
本教程会添加叫做TextClass,FontClass和FontShaderClass的新类。FontShaderClass是用于绘制字体的shader,类似于上一个教程中绘制图像的TextureShaderClass类。FontClass 保存字体数据以及构建绘制文字所需的顶点缓存。TextClass包含每组字符串所需的顶点和索引缓存,它使用FontClass创建句子使用的顶点缓存,然后使用FontShaderClass绘制这些缓存。
Fontclass.h
首先看一下FontClass。这个类加载字体纹理、从文本文件获取字体数据,创建用于字体数据的顶点缓存。文本句子对应的顶点缓存位于TextClass中,而不是在这个类中。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: fontclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _FONTCLASS_H_
#define _FONTCLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
///////////////////////
// MY CLASS INCLUDES //
///////////////////////
#include "textureclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: FontClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class FontClass
{
private:
FontType结构体保存从索引文件读取的索引数据。Left和right是TU纹理坐标。Size表示字符以像素为单位的宽度。
struct FontType
{
float left, right;
int size;
};
VertexType结构体用于构建绘制字符的矩形的顶点数据。一个字符需要两个三角形构成一个矩形,这些三角形都有位置和纹理数据。
struct VertexType
{
D3DXVECTOR3 position;
D3DXVECTOR2 texture;
};
public:
FontClass();
FontClass(const FontClass&);
~FontClass();
bool Initialize(ID3D10Device*, char*, WCHAR*);
void Shutdown();
ID3D10ShaderResourceView* GetTexture();
BuildVertexArray方法生成并返回三角形的顶点数组,它会被TextClass调用创建句子所需的顶点缓存。
void BuildVertexArray(void*, char*, float, float); private: bool LoadFontData(char*); void ReleaseFontData(); bool LoadTexture(ID3D10Device*, WCHAR*); void ReleaseTexture(); private: FontType* m_Font; TextureClass* m_Texture; }; #endif
Fontclass.cpp
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: fontclass.cpp /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "fontclass.h"
在构造函数中将所有私有变量初始化为null。
FontClass::FontClass()
{
m_Font = 0;
m_Texture = 0;
}
FontClass::FontClass(const FontClass& other)
{
}
FontClass::~FontClass()
{
}
Initialize方法中加载字体数据和字体纹理。
bool FontClass::Initialize(ID3D10Device* device, char* fontFilename, WCHAR* textureFilename)
{
bool result;
// Load in the text file containing the font data.
result = LoadFontData(fontFilename);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Load the texture that has the font characters on it.
result = LoadTexture(device, textureFilename);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
Shutdown方法释放字体数据和字体纹理。
void FontClass::Shutdown()
{
// Release the font texture.
ReleaseTexture();
// Release the font data.
ReleaseFontData();
return;
}
在LoadFontData方法中我们加载包含了纹理索引信息的fontdata.txt文件。
bool FontClass::LoadFontData(char* filename)
{
ifstream fin;
int i;
char temp;
首先创建一个FontType结构体数组,数组大小设置为95,即纹理中字符的数量,也就是fontdata.txt文件中索引的数量。
// Create the font spacing buffer.
m_Font = new FontType[95];
if(!m_Font)
{
return false;
}
现在打开文件,将每一行的内容读取到数组m_Font中。我们只需读取纹理TU的left和right坐标和字符的宽度。
// Read in the font size and spacing between chars.
fin.open(filename);
if(fin.fail())
{
return false;
}
// Read in the 95 used ascii characters for text.
for(i=0; i<95; i++)
{
fin.get(temp);
while(temp != ' ')
{
fin.get(temp);
}
fin.get(temp);
while(temp != ' ')
{
fin.get(temp);
}
fin >> m_Font[i].left;
fin >> m_Font[i].right;
fin >> m_Font[i].size;
}
// Close the file.
fin.close();
return true;
}
ReleaseFontData方法释放保存纹理索引数据的数组。
void FontClass::ReleaseFontData()
{
// Release the font data array.
if(m_Font)
{
delete [] m_Font;
m_Font = 0;
}
return;
}
LoadTexture方法读取font.dds文件,从这个纹理文件中获取字符并将字符写入到矩形多边形中进行绘制。
bool FontClass::LoadTexture(ID3D10Device* device, WCHAR* filename)
{
bool result;
// Create the texture object.
m_Texture = new TextureClass;
if(!m_Texture)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the texture object.
result = m_Texture->Initialize(device, filename);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
ReleaseTexture方法释放字体纹理。
void FontClass::ReleaseTexture()
{
// Release the texture object.
if(m_Texture)
{
m_Texture->Shutdown();
delete m_Texture;
m_Texture = 0;
}
return;
}
GetTexture返回字体纹理接口用于绘制。
ID3D10ShaderResourceView* FontClass::GetTexture()
{
return m_Texture->GetTexture();
}
BuildVertexArray被TextClass调用创建文本的顶点缓存。通过这个方法,TextClass中的每个句子就拥有了自己的顶点缓存。输入的参数vertices指向顶点数组,这个数组在创建后发送到TextClass。输入的参数sentence是用来创建顶点数组的文本句子。drawX和drawY为文本的屏幕坐标。
void FontClass::BuildVertexArray(void* vertices, char* sentence, float drawX, float drawY)
{
VertexType* vertexPtr;
int numLetters, index, i, letter;
// Coerce the input vertices into a VertexType structure.
vertexPtr = (VertexType*)vertices;
// Get the number of letters in the sentence.
numLetters = (int)strlen(sentence);
// Initialize the index to the vertex array.
index = 0;
下面的循环过程创建顶点和索引数组。它获取句子中的每个字符并创建了两个三角形,然后使用m_Font数组(包含了纹理TU坐标和像素大小)将字体纹理中的字符映射到这两个三角形中。创建了字符多边形后,更新下一个字符的屏幕X坐标。
// Draw each letter onto a quad.
for(i=0; i<numLetters; i++)
{
letter = ((int)sentence[i]) - 32;
// If the letter is a space then just move over three pixels.
if(letter == 0)
{
drawX = drawX + 3.0f;
}
else
{
// First triangle in quad.
vertexPtr[index].position = D3DXVECTOR3(drawX, drawY, 0.0f); // Top left.
vertexPtr[index].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(m_Font[letter].left, 0.0f);
index++;
vertexPtr[index].position = D3DXVECTOR3((drawX + m_Font[letter].size), (drawY - 16), 0.0f); // Bottom right.
vertexPtr[index].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(m_Font[letter].right, 1.0f);
index++;
vertexPtr[index].position = D3DXVECTOR3(drawX, (drawY - 16), 0.0f); // Bottom left.
vertexPtr[index].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(m_Font[letter].left, 1.0f);
index++;
// Second triangle in quad.
vertexPtr[index].position = D3DXVECTOR3(drawX, drawY, 0.0f); // Top left.
vertexPtr[index].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(m_Font[letter].left, 0.0f);
index++;
vertexPtr[index].position = D3DXVECTOR3(drawX + m_Font[letter].size, drawY, 0.0f); // Top right.
vertexPtr[index].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(m_Font[letter].right, 0.0f);
index++;
vertexPtr[index].position = D3DXVECTOR3((drawX + m_Font[letter].size), (drawY - 16), 0.0f); // Bottom right.
vertexPtr[index].texture = D3DXVECTOR2(m_Font[letter].right, 1.0f);
index++;
// Update the x location for drawing by the size of the letter and one pixel.
drawX = drawX + m_Font[letter].size + 1.0f;
}
}
return;
}
Font.fx
Font.fx是用于绘制2D文字的shader,它只是绘制2D图像的texture.fx改编版本。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: font.fx //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ///////////// // GLOBALS // ///////////// matrix worldMatrix; matrix viewMatrix; matrix projectionMatrix; Texture2D shaderTexture;
这个shader中多了一个新变量pixelColor。这个变量控制字体的颜色。
float4 pixelColor;
///////////////////
// SAMPLE STATES //
///////////////////
SamplerState SampleType
{
Filter = MIN_MAG_MIP_LINEAR;
AddressU = Wrap;
AddressV = Wrap;
};
这个shader的第二个变化是多了一个叫做AlphaBlendingState的混合状态。Blending让字体和背景的3D对象混合在一起。如果没有打开混合,我们会看到文字下面的黑色三角形。而如果打开混合,那么只有文字的像素会显示在屏幕上,而三角形完全不可见。用于混合状态的结构体叫做D3D10_BLEND_DESC,这个新混合状态与默认值几乎完全一样,只有一个区别——destination blend设置为invert source alpha。本教程我不准备详细讲解混合,你只需知道本教程需要一个简单的混合才能显示正确。
/////////////////////
// BLENDING STATES //
/////////////////////
BlendState AlphaBlendingState
{
BlendEnable[0] = TRUE;
DestBlend = INV_SRC_ALPHA;
};
//////////////
// TYPEDEFS //
//////////////
struct VertexInputType
{
float4 position : POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct PixelInputType
{
float4 position : SV_POSITION;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Vertex Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
PixelInputType FontVertexShader(VertexInputType input)
{
PixelInputType output;
// Change the position vector to be 4 units for proper matrix calculations.
input.position.w = 1.0f;
// Calculate the position of the vertex against the world, view, and projection matrices.
output.position = mul(input.position, worldMatrix);
output.position = mul(output.position, viewMatrix);
output.position = mul(output.position, projectionMatrix);
// Store the texture coordinates for the pixel shader.
output.tex = input.tex;
return output;
}
FontPixelShader首先采样字体纹理获取像素。如果采样的颜色为黑色则表示是背景而不是字符上的像素,这时我们就将这个像素alpha设置为零,这样在进行混合计算时就不显示这个像素。如果像素的颜色不是黑色则说明是字符上的像素,这时就将这个像素的颜色乘以pixelColor得到最终的像素颜色。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Pixel Shader
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
float4 FontPixelShader(PixelInputType input) : SV_Target
{
float4 color;
// Sample the texture pixel at this location.
color = shaderTexture.Sample(SampleType, input.tex);
// If the color is black on the texture then treat this pixel as transparent.
if(color.r == 0.0f)
{
color.a = 0.0f;
}
// If the color is other than black on the texture then this is a pixel in the font so draw it using the font pixel color.
else
{
color.rgb = pixelColor.rgb;
color.a = 1.0f;
}
return color;
}
FontTechnique中我们需要使用SetBlendState打开alpha混合状态。第一个参数为shader中创建的混合状态,后面两个参数为默认值。注意如果我们打开了混合状态,那么它就会一直作用下去直至另一个shader关闭它为止。改变混合状态的操作代价不菲,因此应避免频繁进行这个操作,代码中应注意让混合状态的操作减到最少。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Technique
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
technique10 FontTechnique
{
pass pass0
{
SetBlendState(AlphaBlendingState, float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), 0xFFFFFFFF);
SetVertexShader(CompileShader(vs_4_0, FontVertexShader()));
SetPixelShader(CompileShader(ps_4_0, FontPixelShader()));
SetGeometryShader(NULL);
}
}
Fontshaderclass.h
FontShaderClass与上一个教程的TextureShaderClass几乎一样,只是多了些绘制字体的代码。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: fontshaderclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _FONTSHADERCLASS_H_
#define _FONTSHADERCLASS_H_
//////////////
// INCLUDES //
//////////////
#include <d3d10.h>
#include <d3dx10.h>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: FontShaderClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class FontShaderClass
{
public:
FontShaderClass();
FontShaderClass(const FontShaderClass&);
~FontShaderClass();
bool Initialize(ID3D10Device*, HWND);
void Shutdown();
void Render(ID3D10Device*, int, D3DXMATRIX, D3DXMATRIX, D3DXMATRIX, ID3D10ShaderResourceView*, D3DXVECTOR4);
private:
bool InitializeShader(ID3D10Device*, HWND, WCHAR*);
void ShutdownShader();
void OutputShaderErrorMessage(ID3D10Blob*, HWND, WCHAR*);
void SetShaderParameters(D3DXMATRIX, D3DXMATRIX, D3DXMATRIX, ID3D10ShaderResourceView*, D3DXVECTOR4);
void RenderShader(ID3D10Device*, int);
private:
ID3D10Effect* m_effect;
ID3D10EffectTechnique* m_technique;
ID3D10InputLayout* m_layout;
ID3D10EffectMatrixVariable* m_worldMatrixPtr;
ID3D10EffectMatrixVariable* m_viewMatrixPtr;
ID3D10EffectMatrixVariable* m_projectionMatrixPtr;
ID3D10EffectShaderResourceVariable* m_texturePtr;
FontShaderClass多了一个指向shader中的pixel color变量的指针。
ID3D10EffectVectorVariable* m_pixelColorPtr; }; #endif
Fontshaderclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: fontshaderclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "fontshaderclass.h"
FontShaderClass::FontShaderClass()
{
m_effect = 0;
m_technique = 0;
m_layout = 0;
m_worldMatrixPtr = 0;
m_viewMatrixPtr = 0;
m_projectionMatrixPtr = 0;
m_texturePtr = 0;
在构造函数中将pixel color指针初始化为null。
m_pixelColorPtr = 0;
}
FontShaderClass::FontShaderClass(const FontShaderClass& other)
{
}
FontShaderClass::~FontShaderClass()
{
}
Initialize方法加载和编译HLSL font shader文件。
bool FontShaderClass::Initialize(ID3D10Device* device, HWND hwnd)
{
bool result;
// Initialize the shader that will be used to draw the triangle.
result = InitializeShader(device, hwnd, L"../Engine/font.fx");
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
Shutdown释放指针和数据。
void FontShaderClass::Shutdown()
{
// Shutdown the shader effect.
ShutdownShader();
return;
}
Render设置shader参数,然后使用font shader绘制缓存,除了多了一个pixelColor参数,代码与TextureShaderClass是相同的。
void FontShaderClass::Render(ID3D10Device* device, int indexCount, D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, D3DXMATRIX viewMatrix,
D3DXMATRIX projectionMatrix, ID3D10ShaderResourceView* texture, D3DXVECTOR4 pixelColor)
{
// Set the shader parameters that it will use for rendering.
SetShaderParameters(worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, texture, pixelColor);
// Now render the prepared buffers with the shader.
RenderShader(device, indexCount);
return;
}
InitializeShader方法加载HLSL font shader,准备指向font shader的指针变量。
bool FontShaderClass::InitializeShader(ID3D10Device* device, HWND hwnd, WCHAR* filename)
{
HRESULT result;
ID3D10Blob* errorMessage;
D3D10_INPUT_ELEMENT_DESC polygonLayout[2];
unsigned int numElements;
D3D10_PASS_DESC passDesc;
// Initialize the error message.
errorMessage = 0;
// Load the shader in from the file.
result = D3DX10CreateEffectFromFile(filename, NULL, NULL, "fx_4_0", D3D10_SHADER_ENABLE_STRICTNESS, 0,
device, NULL, NULL, &m_effect, &errorMessage, NULL);
if(FAILED(result))
{
// If the shader failed to compile it should have writen something to the error message.
if(errorMessage)
{
OutputShaderErrorMessage(errorMessage, hwnd, filename);
}
// If there was nothing in the error message then it simply could not find the shader file itself.
else
{
MessageBox(hwnd, filename, L"Missing Shader File", MB_OK);
}
return false;
}
Technique的名称修改为FontTechnique。
// Get a pointer to the technique inside the shader.
m_technique = m_effect->GetTechniqueByName("FontTechnique");
if(!m_technique)
{
return false;
}
// Now setup the layout of the data that goes into the shader.
// This setup needs to match the VertexType stucture in the ModelClass and in the shader.
polygonLayout[0].SemanticName = "POSITION";
polygonLayout[0].SemanticIndex = 0;
polygonLayout[0].Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT;
polygonLayout[0].InputSlot = 0;
polygonLayout[0].AlignedByteOffset = 0;
polygonLayout[0].InputSlotClass = D3D10_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA;
polygonLayout[0].InstanceDataStepRate = 0;
polygonLayout[1].SemanticName = "TEXCOORD";
polygonLayout[1].SemanticIndex = 0;
polygonLayout[1].Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32_FLOAT;
polygonLayout[1].InputSlot = 0;
polygonLayout[1].AlignedByteOffset = D3D10_APPEND_ALIGNED_ELEMENT;
polygonLayout[1].InputSlotClass = D3D10_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA;
polygonLayout[1].InstanceDataStepRate = 0;
// Get a count of the elements in the layout.
numElements = sizeof(polygonLayout) / sizeof(polygonLayout[0]);
// Get the description of the first pass described in the shader technique.
m_technique->GetPassByIndex(0)->GetDesc(&passDesc);
// Create the input layout.
result = device->CreateInputLayout(polygonLayout, numElements, passDesc.pIAInputSignature, passDesc.IAInputSignatureSize,
&m_layout);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Get pointers to the three matrices inside the shader so we can update them from this class.
m_worldMatrixPtr = m_effect->GetVariableByName("worldMatrix")->AsMatrix();
m_viewMatrixPtr = m_effect->GetVariableByName("viewMatrix")->AsMatrix();
m_projectionMatrixPtr = m_effect->GetVariableByName("projectionMatrix")->AsMatrix();
// Get pointer to the texture resource inside the shader.
m_texturePtr = m_effect->GetVariableByName("shaderTexture")->AsShaderResource();
获取指向shader中的pixelColor变量的指针。
// Get pointer to the pixel color variable inside the shader.
m_pixelColorPtr = m_effect->GetVariableByName("pixelColor")->AsVector();
return true;
}
ShutdownShader方法释放所有shader相关的数据。
void FontShaderClass::ShutdownShader()
{
新的pixel color指针在这里释放。
// Release the pointer to the pixel color of the font.
m_pixelColorPtr = 0;
// Release the pointer to the texture in the shader file.
m_texturePtr = 0;
// Release the pointers to the matrices inside the shader.
m_worldMatrixPtr = 0;
m_viewMatrixPtr = 0;
m_projectionMatrixPtr = 0;
// Release the pointer to the shader layout.
if(m_layout)
{
m_layout->Release();
m_layout = 0;
}
// Release the pointer to the shader technique.
m_technique = 0;
// Release the pointer to the shader.
if(m_effect)
{
m_effect->Release();
m_effect = 0;
}
return;
}
OutputShaderErrorMessage将shader编译过程中的错误信息写入到一个文本文件。
void FontShaderClass::OutputShaderErrorMessage(ID3D10Blob* errorMessage, HWND hwnd, WCHAR* shaderFilename)
{
char* compileErrors;
unsigned long bufferSize, i;
ofstream fout;
// Get a pointer to the error message text buffer.
compileErrors = (char*)(errorMessage->GetBufferPointer());
// Get the length of the message.
bufferSize = errorMessage->GetBufferSize();
// Open a file to write the error message to.
fout.open("shader-error.txt");
// Write out the error message.
for(i=0; i<bufferSize; i++)
{
fout << compileErrors[i];
}
// Close the file.
fout.close();
// Release the error message.
errorMessage->Release();
errorMessage = 0;
// Pop a message up on the screen to notify the user to check the text file for compile errors.
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Error compiling shader. Check shader-error.txt for message.", shaderFilename, MB_OK);
return;
}
SetShaderParameters方法设置所有shader变量。
void FontShaderClass::SetShaderParameters(D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, D3DXMATRIX viewMatrix, D3DXMATRIX projectionMatrix,
ID3D10ShaderResourceView* texture, D3DXVECTOR4 pixelColor)
{
// Set the world matrix variable inside the shader.
m_worldMatrixPtr->SetMatrix((float*)&worldMatrix);
// Set the view matrix variable inside the shader.
m_viewMatrixPtr->SetMatrix((float*)&viewMatrix);
// Set the projection matrix variable inside the shader.
m_projectionMatrixPtr->SetMatrix((float*)&projectionMatrix);
// Bind the texture.
m_texturePtr->SetResource(texture);
pixelColor shader变量在这里被设置。
// Set the pixel color variable inside the shader with the pixelColor vector. m_pixelColorPtr->SetFloatVector((float*)&pixelColor); return; }
RenderShader使用font shader绘制顶点/索引缓存。
void FontShaderClass::RenderShader(ID3D10Device* device, int indexCount)
{
D3D10_TECHNIQUE_DESC techniqueDesc;
unsigned int i;
// Set the input layout.
device->IASetInputLayout(m_layout);
// Get the description structure of the technique from inside the shader so it can be used for rendering.
m_technique->GetDesc(&techniqueDesc);
// Go through each pass in the technique (should be just one currently) and renders the triangles.
for(i=0; i<techniqueDesc.Passes; ++i)
{
m_technique->GetPassByIndex(i)->Apply(0);
device->DrawIndexed(indexCount, 0, 0);
}
return;
}
Textclass.h
TextClass处理2D文本的绘制。它在FontClass和FontShaderClass的配合下在屏幕上绘制2D文本。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: textclass.h
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef _TEXTCLASS_H_
#define _TEXTCLASS_H_
///////////////////////
// MY CLASS INCLUDES //
///////////////////////
#include "fontclass.h"
#include "fontshaderclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: TextClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class TextClass
{
private:
SentenceType结构体保存文本句子的信息。
struct SentenceType
{
ID3D10Buffer *vertexBuffer, *indexBuffer;
int vertexCount, indexCount, maxLength;
float red, green, blue;
};
VertexType必须与FontClass类中的VertexType匹配。
struct VertexType
{
D3DXVECTOR3 position;
D3DXVECTOR2 texture;
};
public:
TextClass();
TextClass(const TextClass&);
~TextClass();
bool Initialize(ID3D10Device*, HWND, int, int, D3DXMATRIX);
void Shutdown();
void Render(ID3D10Device*, D3DXMATRIX, D3DXMATRIX);
private:
bool InitializeSentence(SentenceType**, int, ID3D10Device*);
bool UpdateSentence(SentenceType*, char*, int, int, float, float, float);
void ReleaseSentence(SentenceType**);
void RenderSentence(ID3D10Device*, SentenceType*, D3DXMATRIX, D3DXMATRIX);
private:
FontClass* m_Font;
FontShaderClass* m_FontShader;
int m_screenWidth, m_screenHeight;
D3DXMATRIX m_baseViewMatrix;
本教程中我们使用两个句子。
SentenceType* m_sentence1; SentenceType* m_sentence2; }; #endif
Textclass.cpp
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: textclass.cpp /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "textclass.h"
构造函数将私有变量初始化为null。
TextClass::TextClass()
{
m_Font = 0;
m_FontShader = 0;
m_sentence1 = 0;
m_sentence2 = 0;
}
TextClass::TextClass(const TextClass& other)
{
}
TextClass::~TextClass()
{
}
bool TextClass::Initialize(ID3D10Device* device, HWND hwnd, int screenWidth, int screenHeight, D3DXMATRIX baseViewMatrix)
{
bool result;
保存屏幕大小和基视矩阵用于绘制2D文本。
// Store the screen width and height. m_screenWidth = screenWidth; m_screenHeight = screenHeight; // Store the base view matrix. m_baseViewMatrix = baseViewMatrix;
创建并初始化font对象。
// Create the font object.
m_Font = new FontClass;
if(!m_Font)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the font object.
result = m_Font->Initialize(device, "../Engine/data/fontdata.txt", L"../Engine/data/font.dds");
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the font object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
创建并初始化font shader对象。
// Create the font shader object.
m_FontShader = new FontShaderClass;
if(!m_FontShader)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the font shader object.
result = m_FontShader->Initialize(device, hwnd);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the font shader object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
创建并初始化本教程要显示的两个句子。一个句子在100, 100处显示Hello,另一个句子在100, 200出显示Goodbye。UpdateSentence方法可以改变句子的内容、位置和字体颜色。
// Initialize the first sentence.
result = InitializeSentence(&m_sentence1, 16, device);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Now update the sentence vertex buffer with the new string information.
result = UpdateSentence(m_sentence1, "Hello", 100, 100, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the seconnd sentence.
result = InitializeSentence(&m_sentence2, 16, device);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
// Now update the sentence vertex buffer with the new string information.
result = UpdateSentence(m_sentence2, "Goodbye", 100, 200, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
if(!result)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
Shutdown方法释放两个句子、font对象和font shader对象。
void TextClass::Shutdown()
{
// Release the first sentence.
ReleaseSentence(&m_sentence1);
// Release the second sentence.
ReleaseSentence(&m_sentence2);
// Release the font shader object.
if(m_FontShader)
{
m_FontShader->Shutdown();
delete m_FontShader;
m_FontShader = 0;
}
// Release the font object.
if(m_Font)
{
m_Font->Shutdown();
delete m_Font;
m_Font = 0;
}
return;
}
Render方法在屏幕上绘制两个句子。
void TextClass::Render(ID3D10Device* device, D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, D3DXMATRIX orthoMatrix)
{
// Draw the first sentence.
RenderSentence(device, m_sentence1, worldMatrix, orthoMatrix);
// Draw the second sentence.
RenderSentence(device, m_sentence2, worldMatrix, orthoMatrix);
return;
}
InitializeSentence方法创建一个包含空顶点缓存的SentenceType。参数maxLength确定顶点缓存的大小。所有句子都拥有衣蛾顶点缓存和一个索引缓存,它们必须首先进行初始化。
bool TextClass::InitializeSentence(SentenceType** sentence, int maxLength, ID3D10Device* device)
{
VertexType* vertices;
unsigned long* indices;
D3D10_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc, indexBufferDesc;
D3D10_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexData, indexData;
HRESULT result;
int i;
// Create a new sentence object.
*sentence = new SentenceType;
if(!*sentence)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the sentence buffers to null.
(*sentence)->vertexBuffer = 0;
(*sentence)->indexBuffer = 0;
// Set the maximum length of the sentence.
(*sentence)->maxLength = maxLength;
// Set the number of vertices in the vertex array.
(*sentence)->vertexCount = 6 * maxLength;
// Set the number of indexes in the index array.
(*sentence)->indexCount = (*sentence)->vertexCount;
// Create the vertex array.
vertices = new VertexType[(*sentence)->vertexCount];
if(!vertices)
{
return false;
}
// Create the index array.
indices = new unsigned long[(*sentence)->indexCount];
if(!indices)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize vertex array to zeros at first.
memset(vertices, 0, (sizeof(VertexType) * (*sentence)->vertexCount));
// Initialize the index array.
for(i=0; i<(*sentence)->indexCount; i++)
{
indices[i] = i;
}
在创建顶点缓存描述时将Usage设置为动态,这样我们就可以在任何时候改变句子的内容。
// Set up the description of the dynamic vertex buffer.
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D10_USAGE_DYNAMIC;
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(VertexType) * (*sentence)->vertexCount;
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D10_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D10_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE;
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
// Give the subresource structure a pointer to the vertex data.
vertexData.pSysMem = vertices;
// Create the vertex buffer.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&vertexBufferDesc, &vertexData, &(*sentence)->vertexBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
索引缓存是一个常规的静态缓存,因为它的内容不会变化。
// Set up the description of the static index buffer.
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D10_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(unsigned long) * (*sentence)->indexCount;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D10_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
// Give the subresource structure a pointer to the index data.
indexData.pSysMem = indices;
// Create the index buffer.
result = device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &indexData, &(*sentence)->indexBuffer);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Release the vertex array as it is no longer needed.
delete [] vertices;
vertices = 0;
// Release the index array as it is no longer needed.
delete [] indices;
indices = 0;
return true;
}
UpdateSentence可以改变顶点缓存的内容。这个方法使用Map和Unmap方法以及memcpy更新顶点缓存的内容。
bool TextClass::UpdateSentence(SentenceType* sentence, char* text, int positionX, int positionY, float red, float green, float blue)
{
int numLetters;
VertexType* vertices;
float drawX, drawY;
void* verticesPtr;
HRESULT result;
设置句子的颜色和长度。
// Store the color of the sentence.
sentence->red = red;
sentence->green = green;
sentence->blue = blue;
// Get the number of letters in the sentence.
numLetters = (int)strlen(text);
// Check for possible buffer overflow.
if(numLetters > sentence->maxLength)
{
return false;
}
// Create the vertex array.
vertices = new VertexType[sentence->vertexCount];
if(!vertices)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize vertex array to zeros at first.
memset(vertices, 0, (sizeof(VertexType) * sentence->vertexCount));
计算句子的开始位置。
// Calculate the X and
Y pixel position on the screen to start drawing to. drawX =
(float)(((m_screenWidth / 2) * -1) + positionX); drawY = (float)((m_screenHeight
/ 2) - positionY);
使用FontClass类和句子信息构建顶点数组。
// Calculate the X and Y pixel position on the screen to start drawing to. drawX = (float)(((m_screenWidth / 2) * -1) + positionX); drawY = (float)((m_screenHeight / 2) - positionY); // Use the font class to build the vertex array from the sentence text and sentence draw location. m_Font->BuildVertexArray((void*)vertices, text, drawX, drawY);
将顶点数组的内复制到顶点缓存中。
// Initialize the vertex buffer pointer to null first.
verticesPtr = 0;
// Lock the vertex buffer.
result = sentence->vertexBuffer->Map(D3D10_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, (void**)&verticesPtr);
if(FAILED(result))
{
return false;
}
// Copy the vertex array into the vertex buffer.
memcpy(verticesPtr, (void*)vertices, (sizeof(VertexType) * sentence->vertexCount));
// Unlock the vertex buffer.
sentence->vertexBuffer->Unmap();
// Release the vertex array as it is no longer needed.
delete [] vertices;
vertices = 0;
return true;
}
ReleaseSentence用来释放顶点。索引缓存和sentence对象。
void TextClass::ReleaseSentence(SentenceType** sentence)
{
if(*sentence)
{
// Release the sentence vertex buffer.
if((*sentence)->vertexBuffer)
{
(*sentence)->vertexBuffer->Release();
(*sentence)->vertexBuffer = 0;
}
// Release the sentence index buffer.
if((*sentence)->indexBuffer)
{
(*sentence)->indexBuffer->Release();
(*sentence)->indexBuffer = 0;
}
// Release the sentence.
delete *sentence;
*sentence = 0;
}
return;
}
RenderSentence方法设置顶点和索引缓存并调用FontShaderClass对象绘制句子。注意我们使用m_baseViewMatrix代替当前的视矩阵,这可以让我们无视当前视矩阵的位置在相同的位置绘制文本。我们还使用orthoMatrix代替常规的投影矩阵,因为我们使用的是2D坐标。
void TextClass::RenderSentence(ID3D10Device* device, SentenceType* sentence, D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, D3DXMATRIX orthoMatrix)
{
unsigned int stride, offset;
D3DXVECTOR4 pixelColor;
// Set vertex buffer stride and offset.
stride = sizeof(VertexType);
offset = 0;
// Set the vertex buffer to active in the input assembler so it can be rendered.
device->IASetVertexBuffers(0, 1, &sentence->vertexBuffer, &stride, &offset);
// Set the index buffer to active in the input assembler so it can be rendered.
device->IASetIndexBuffer(sentence->indexBuffer, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
// Set the type of primitive that should be rendered from this vertex buffer, in this case triangles.
device->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D10_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
// Create a pixel color vector with the input sentence color.
pixelColor = D3DXVECTOR4(sentence->red, sentence->green, sentence->blue, 1.0f);
// Render the text using the font shader.
m_FontShader->Render(device, sentence->indexCount, worldMatrix, m_baseViewMatrix, orthoMatrix, m_Font->GetTexture(), pixelColor);
return;
}
Graphicsclass.h
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Filename: graphicsclass.h //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifndef _GRAPHICSCLASS_H_ #define _GRAPHICSCLASS_H_ ///////////// // GLOBALS // ///////////// const bool FULL_SCREEN = true; const bool VSYNC_ENABLED = true; const float SCREEN_DEPTH = 1000.0f; const float SCREEN_NEAR = 0.1f; /////////////////////// // MY CLASS INCLUDES // /////////////////////// #include "d3dclass.h" #include "cameraclass.h"
现在需要包含新类TextClass的头文件。
#include "textclass.h"
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Class name: GraphicsClass
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class GraphicsClass
{
public:
GraphicsClass();
GraphicsClass(const GraphicsClass&);
~GraphicsClass();
bool Initialize(int, int, HWND);
void Shutdown();
void Frame();
bool Render();
private:
D3DClass* m_D3D;
CameraClass* m_Camera;
定义一个新私有变量用于TextClass对象。
TextClass* m_Text; }; #endif
Graphicsclass.cpp
我们仅关注相对于上一个教程有所变化的代码。
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Filename: graphicsclass.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "graphicsclass.h"
GraphicsClass::GraphicsClass()
{
m_D3D = 0;
m_Camera = 0;
m_Text = 0;
}
GraphicsClass::GraphicsClass(const GraphicsClass& other)
{
}
GraphicsClass::~GraphicsClass()
{
}
bool GraphicsClass::Initialize(int screenWidth, int screenHeight, HWND hwnd)
{
bool result;
D3DXMATRIX baseViewMatrix;
// Create the Direct3D object.
m_D3D = new D3DClass;
if(!m_D3D)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the Direct3D object.
result = m_D3D->Initialize(screenWidth, screenHeight, VSYNC_ENABLED, hwnd, FULL_SCREEN, SCREEN_DEPTH, SCREEN_NEAR);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize Direct3D.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
// Create the camera object.
m_Camera = new CameraClass;
if(!m_Camera)
{
return false;
}
我们创建了一个新的视矩阵用于TextClass,这样文本才能总是绘制在屏幕的同一位置而不会随相机位置的变化而变化。
// Initialize a base view matrix with the camera for 2D user interface rendering. m_Camera->SetPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f); m_Camera->Render(); m_Camera->GetViewMatrix(baseViewMatrix);
下面的代码创建并初始化TextClass对象。
// Create the text object.
m_Text = new TextClass;
if(!m_Text)
{
return false;
}
// Initialize the text object.
result = m_Text->Initialize(m_D3D->GetDevice(), hwnd, screenWidth, screenHeight, baseViewMatrix);
if(!result)
{
MessageBox(hwnd, L"Could not initialize the text object.", L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
return true;
}
void GraphicsClass::Shutdown()
{
下面的代码释放TextClass对象。
// Release the text object.
if(m_Text)
{
m_Text->Shutdown();
delete m_Text;
m_Text = 0;
}
// Release the camera object.
if(m_Camera)
{
delete m_Camera;
m_Camera = 0;
}
// Release the Direct3D object.
if(m_D3D)
{
m_D3D->Shutdown();
delete m_D3D;
m_D3D = 0;
}
return;
}
void GraphicsClass::Frame()
{
// Set the position of the camera.
m_Camera->SetPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, -10.0f);
return;
}
bool GraphicsClass::Render()
{
D3DXMATRIX worldMatrix, viewMatrix, projectionMatrix, orthoMatrix;
// Clear the buffers to begin the scene.
m_D3D->BeginScene(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
// Generate the view matrix based on the camera's position.
m_Camera->Render();
// Get the world, view, projection, and ortho matrices from the camera and d3d objects.
m_D3D->GetWorldMatrix(worldMatrix);
m_Camera->GetViewMatrix(viewMatrix);
m_D3D->GetProjectionMatrix(projectionMatrix);
m_D3D->GetOrthoMatrix(orthoMatrix);
// Turn off the Z buffer to begin all 2D rendering.
m_D3D->TurnZBufferOff();
调用text对象绘制文本句子。和2D图像一样,我们需要在绘制前关闭Z缓存,在绘制后重新开启Z缓存。
// Render the text strings. m_Text->Render(m_D3D->GetDevice(), worldMatrix, orthoMatrix); // Turn the Z buffer back on now that all 2D rendering has completed. m_D3D->TurnZBufferOn(); // Present the rendered scene to the screen. m_D3D->EndScene(); return true; }
总结
现在我们就可以在任意位置绘制有颜色的文本了。

练习
1.编译程序在屏幕的100x100位置显示白色的“Hello”,它的下面是黄色的“Goodbye”。
2.改变句子的内容、颜色和位置。
3.创建第三个句子加以显示。
4.注释掉font.fx中的SetBlendState(AlphaBlendingState, float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), 0xFFFFFFFF),将GraphicsClass::Render文件中的代码修改为m_D3D->BeginScene(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);,观察屏幕上的结果,理解为什么需要混合。
5.取消对SetBlendState(AlphaBlendingState, float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), 0xFFFFFFFF)的注释,但仍保持m_D3D->BeginScene(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);,看看显示结果的不同。
文件下载(已下载 993 次)发布时间:2012/7/24 上午12:24:36 阅读次数:10198
